Recent Discoveries and New Interpretations
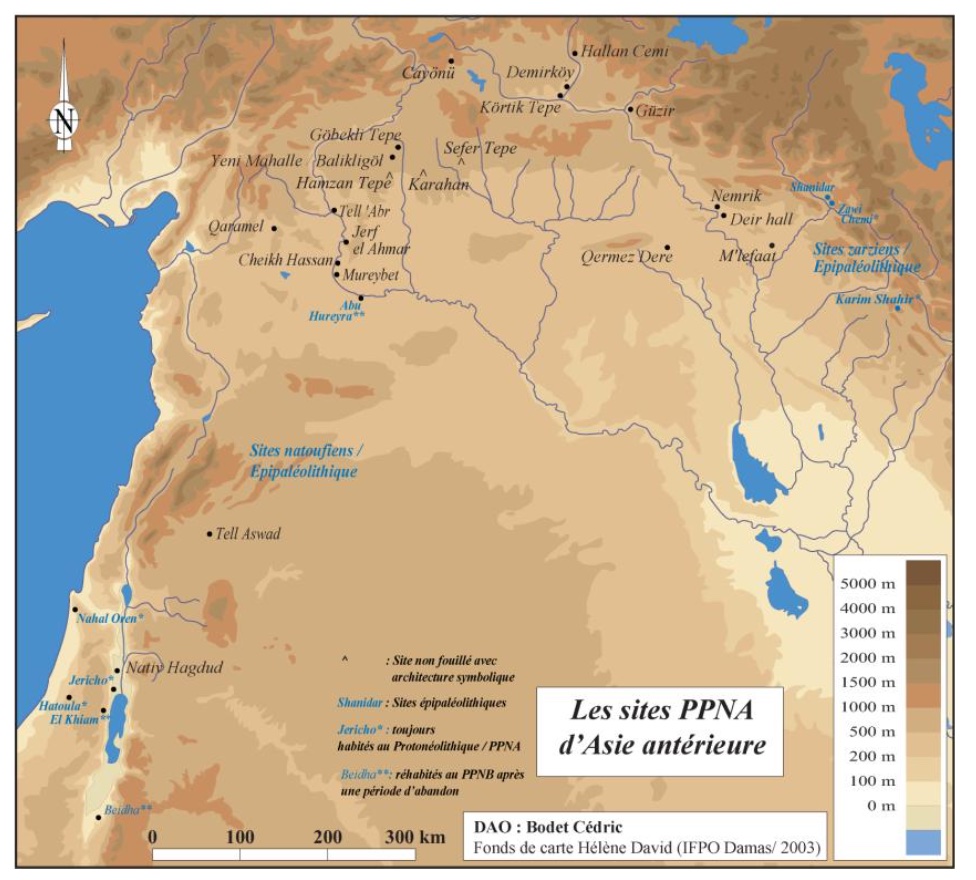
The most famous Pre-pottery Neolithic site of Anatolia, Göbekli Tepe, since 1994 has been the subject of intensive studies due to its peculiar characteristics, linked to the presence of both circular buildings and the so-called anthropomorphic T-shaped pillars. It was supposed that its discovery would have been one of a kind, but in the next few years scholars revealed the existence of similar settlements in the area of Şanlıurfa Province. These sites, still far from being investigated, share with Göbekli Tepe the same archaeological evidences, including chronological features, size and architectural and iconographic traits. The aim of this article is to focus on the new available data, which could lead us to re-discuss the interpretive models valid up to a few years ago, as recent publications point out. New inter- pretive tools and excavations are required to better understand what seems to be the clue of the presence of a real cultural facies with precise connotations, amongst which an high specialized craftmanship, that was able to exploit the best limestone morphology of the territory for the construction of monumental complexes.


